Motor Vibration
Published: March 18, 2018
By: Felix Rodriguez, Equipment Specialist
Types of problems related to rotating equipment
A wide variety of problems in rotating equipment can be causes of motor vibration which can lead to issues like:
- Unbalance (When there is a voltage difference between the phases of a three-phase system).
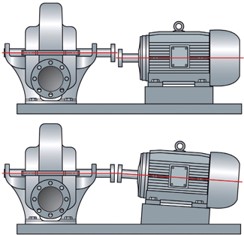
- Misalignment (When there is a angular misalignment where the motor shaft is under an angle with the pump shaft).
- Mechanical Looseness (When there is loose bolts which cause the fit to be loose between the sleeve bearing components).
- Bearing (When lubrication is needed to reduced friction between moving parts such as the shaft rotating).
- Vibration (When motor is imbalanced, misaligned and loose all rotating components shift it’s weight).
- Gears (When components create a grinding noise due to shifting).
- Electrical (When low resistance occurs, due to overheating, corrosion or physical damage of internal components).
- Belt Drive (When the belt is loose and causes slippage, which leads to friction and belt cracking or breaking).
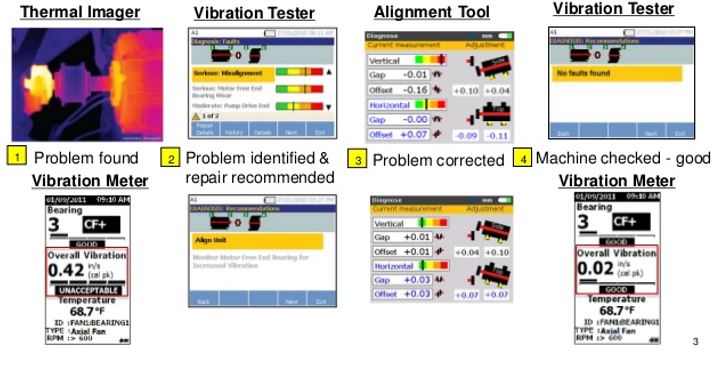
Example of finding and fixing a misalignment problem
Step 1: Find the problem using a thermal image camera or vibration meter.
Step 2: Use the vibration tester to diagnose, identify the severity and repair recommendation.
Step 3: Be proactive; in generating the work order and sharing your findings with others.
Step 4: Correct the problem with the necessary alignment tool.
Step 5: Use the vibration tester and vibration meter to confirm the problem was fixed.
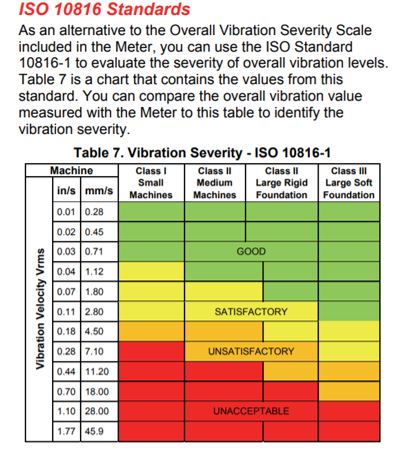
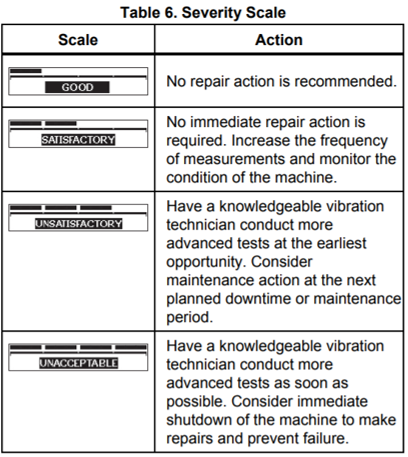
Vibration Screening Tools
In a predictive maintenance program, it is necessary to establish a severity criteria or limits above which actions should be taken. With the understanding of machine design and operation and a vibration signature analysis, one can interpret the machine problem at the component level.